This is my first time writing a blog and the start of my journey of learning in public and contributing something good to society and the open source community.
In this blog, I will share my knowledge about the basics of computer networking.
computer: commonly oriented machine particularly used for training and research.
Now you may wonder what is the internet? what are these protocols? what is www?
I'll explain it you first what is the internet?
The Internet is a collection of different computers connecting with computers on a global scale or we can say it is a collection of computer networks.
Protocols: protocols are a set of rules for how data is transferred over the internet, meaning protocol enables computers to communicate with one another, basically how data is sent and received comes under protocol, it is developed by the Internet society.
WWW: world wide web developed by tim burners, allows access to all the documents and links present all over the internet.
Q. What is a web server?
A web server is software and hardware that uses HTTP and other protocols to respond to clients' requests made over the world wide web. The main job of a web server is to display website content through storing processing and delivering web pages to users.
e.g
sending and receiving emails.
building and publishing web pages.
PROTOCOLS
There are different types of protocols for how data is transferred over the internet,
e.g.
TCP: transmission control protocol (the data will reach its destination and will not be lost or corrupted on the way)
UDP: user datagram protocol (when you don't care about 100% of data reaching the client) e.g. video conferencing.
HTTP: hypertext transfer protocol (used by web browsers) when a client sends a request to the server the server will send a response back all of these are given inside HTTP, how the server will send back the data.
Server and Client
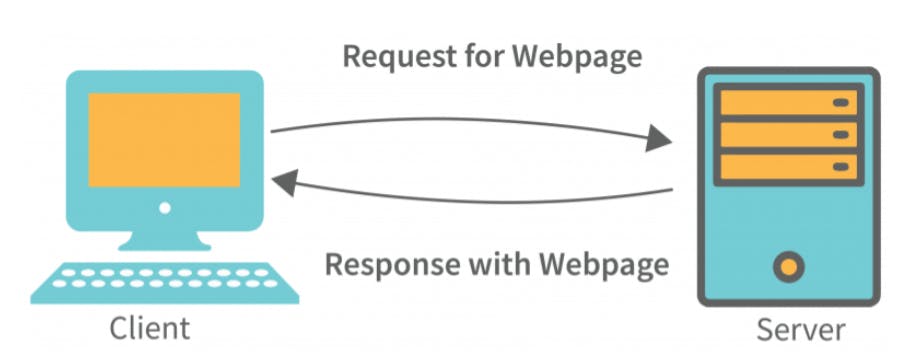
this is a client-and-server architecture in which the client sends a request to the server and the server responds with a web page.
DATA : we get data in packets(chunks of data) a network packet is a basic unit of data that is grouped together and transferred over a computer network.
* Packets contain header (contains origin and destination IP address) and Payload (the actual data).
IP-address: A unique address that identifies a device on the internet
consisting of..
[x.x.x.x.] ---------> every x ranges between 0-225
for example, the IP address of one of Google's servers is 172.217.1.46
Google has many servers and all have different IP addresses, if we write google.com it will be resolved to a particular IP address.
Every device has a unique IP address by which it can be identified.
The IP address has 2 functions :
network interface identification(unique identification of interface between device &network).
local addressing.
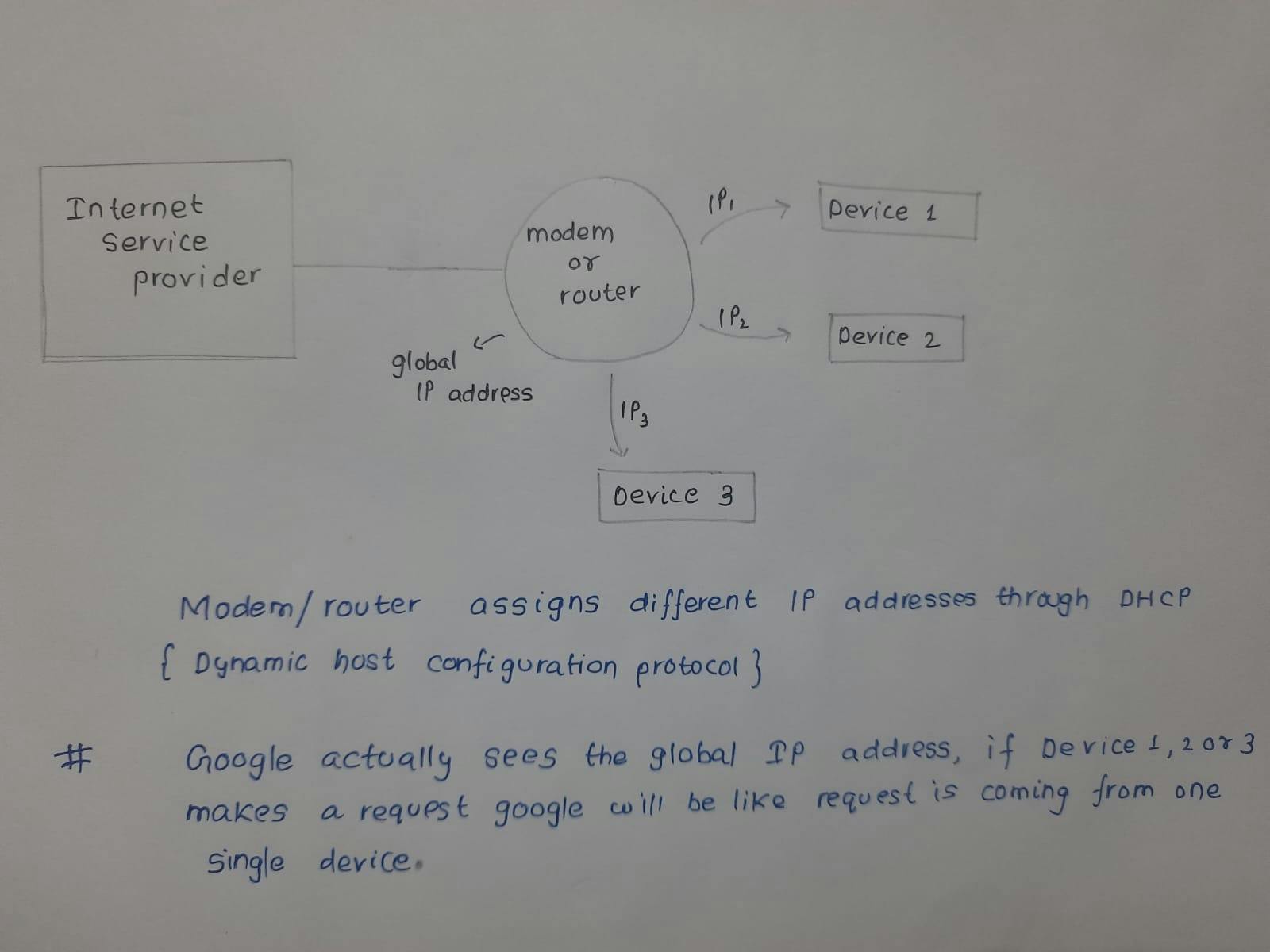
This is actually how routers work
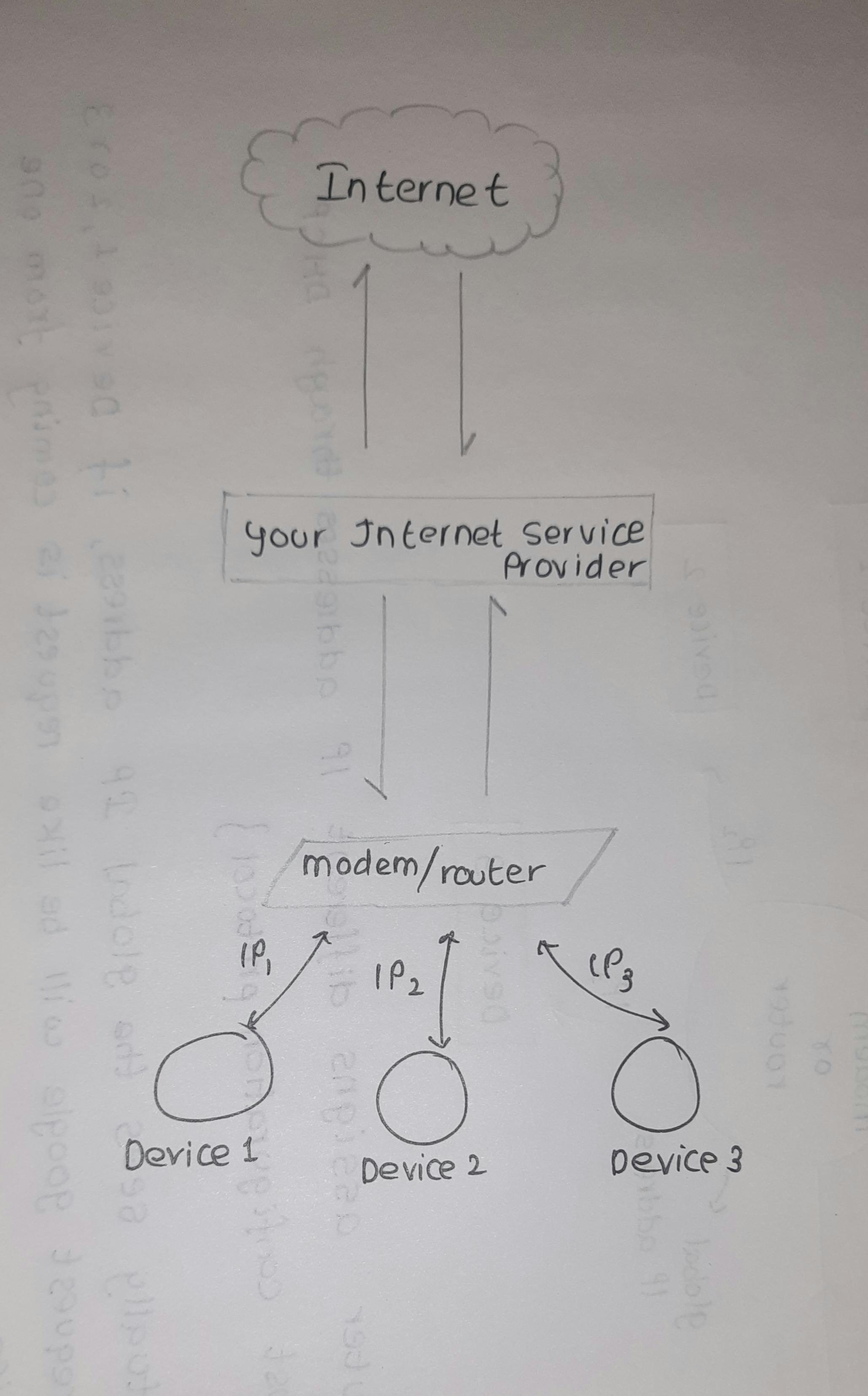
If a client made a request, now this router will decide who had the request D1,D2 or D3 it does it using NAT(network access translator) it will be like hey D1 had Chrome open in their device and it requested something.
Now modem is like I know D1 made the request but which application in D1 made the request e.g. (you are running Mongo DB you made a request and you want the data to be back in Mongo DB)
IP address decides which device to send the data to, but how do we decide which application to send the data in that device?
we do that by using PORTS because one single computer can be running various applications all of these will be having same IP address because they are in the same device but they will have different port numbers.
{ If you are talking to your friend using a chat application so you will be having an IP address and a port number, the IP address will determine where your computers are located and the port number will determine which application you two are using to communicate.}
Port number: Port numbers are used to determine what protocol incoming traffic should be divided to, which means it identifies a specific process to which a message is to be forwarded when it arrives at the server.
e.g. HTTP will happen on port 80
0 - 1023: reserved port numbers
1024-49151: registered for applications like my SQL Mongo DB etc.
(remaining ones you can use)
Now let's learn about networking devices
Repeater: A repeater amplifies and regenerates the signals over wide distances, when the signal becomes weak repeater copies it and regenerates it bit by bit (a single bit is 0 or 1 ) repeater has 2 ports.
Bridge: A bridge is a repeater, with add on the functionality of filtering content by reading the MAC addresses of the source and destination. It is also a 2-port device.
Hub: It is a multiport repeater a hub connects multiple wires coming from different branches, for example, the connector in star topology which connects different stations. Hubs cannot filter data, so data packets are sent to all connected devices. (we will learn about topologies in the later section of the blog)
Switch: A switch can perform error checking before forwarding data, which makes it very efficient as it does not forward packets that have errors and forward good packets selectively to the correct port only.
Routers: A router is a device like a switch that routes data packets based on their IP addresses. Data packets contain header and payload header contains information about the IP address router reads them and routes the packets to the destination.
Gateway: Gateway is called a protocol converter it converts different protocols into another protocol gateways are generally more complex than switches or routers, they work as messenger agents that take data from one system, interpret it, and transfer it to another system.
These were some networking devices now we will learn about topologies:
Topology : It is arrangement of connections within a network there are different types of topologies:
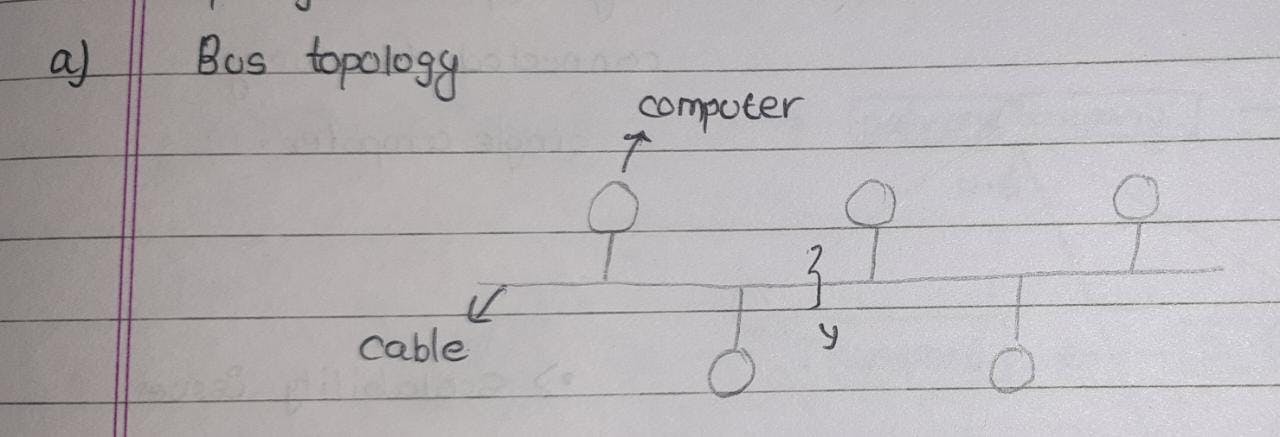
- Bus topology : All the computers are connected through a main cable. major disadvantage is if the main cable breaks the rest of the computers are disconnected.
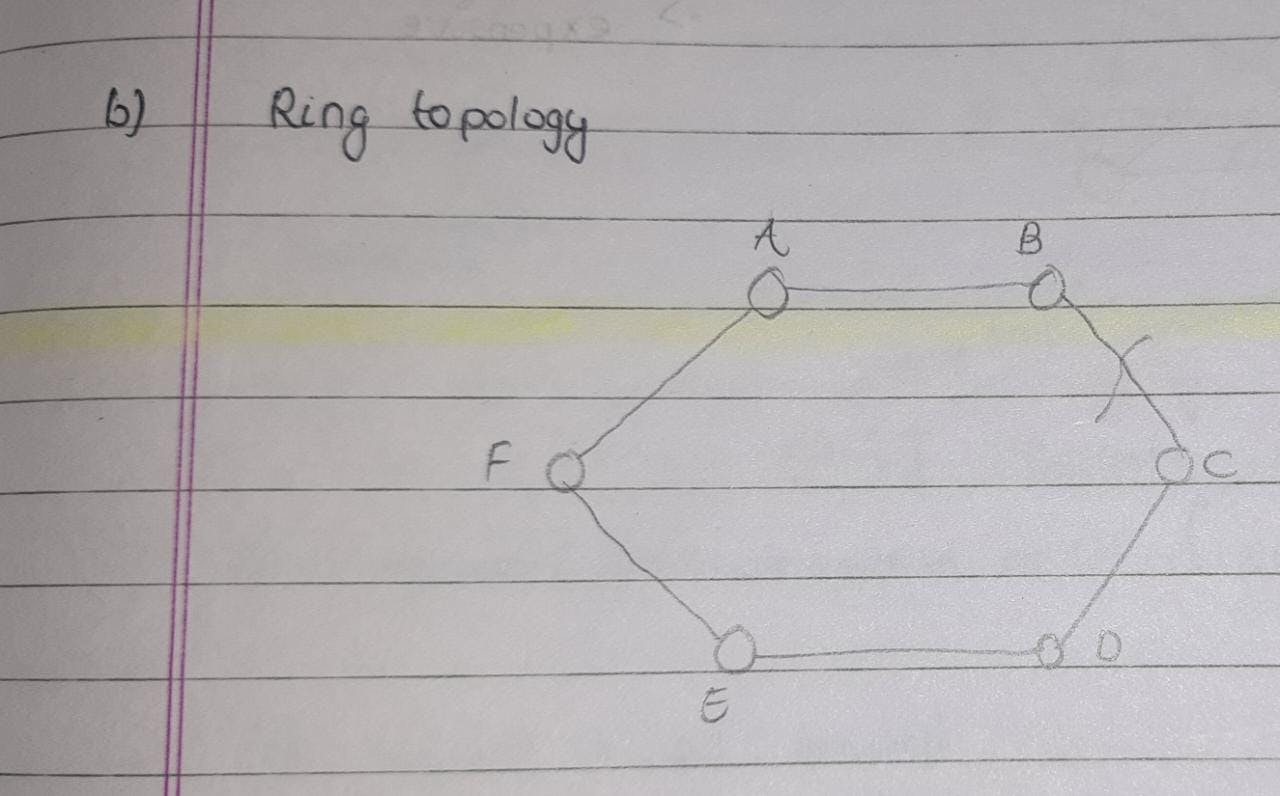
Ring topology: In a ring topology, every system communicates with one another.
Limitations: 1) if the cable breaks you will not be able to transfer data.
2) a lot of unnecessary calls are being made for example you want to send data from A to D it's making calls to B and c also.
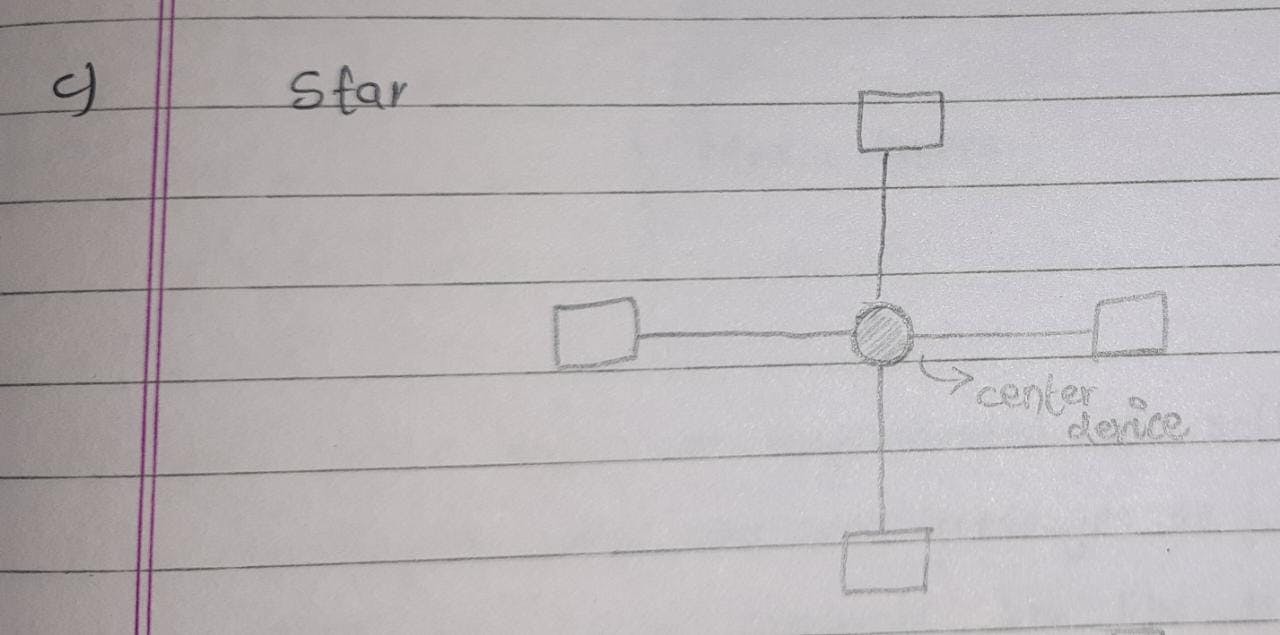
Star topology: A central device is connected to all the computers.
Limitation: if the central device fails the network goes down.
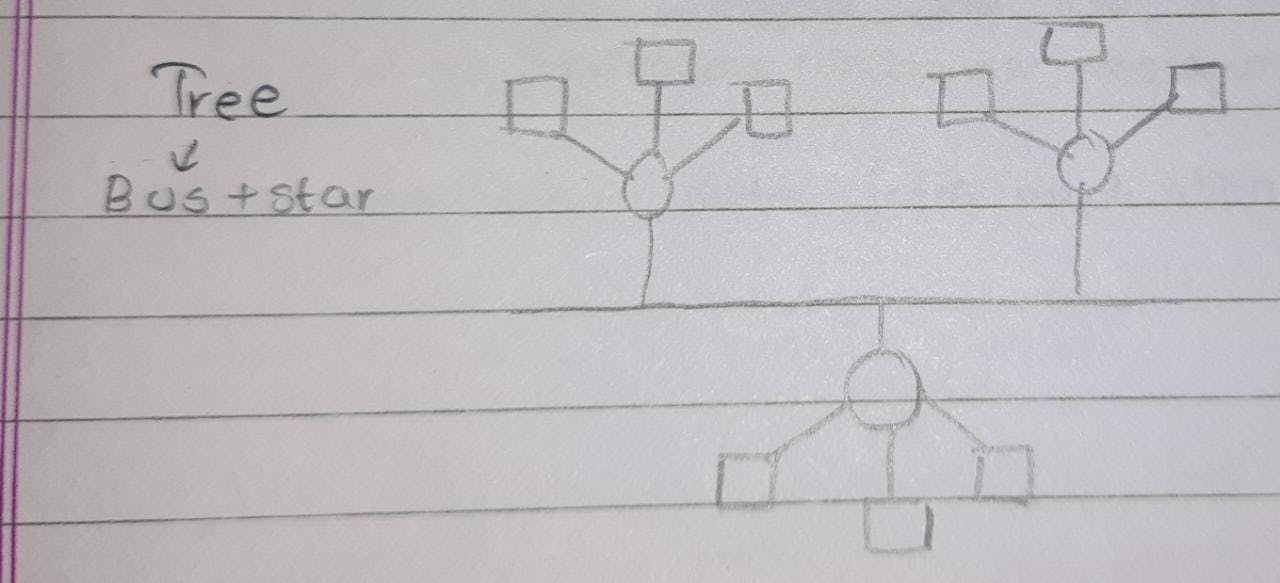
Tree topology: it is a combination of bus topology and star topology.
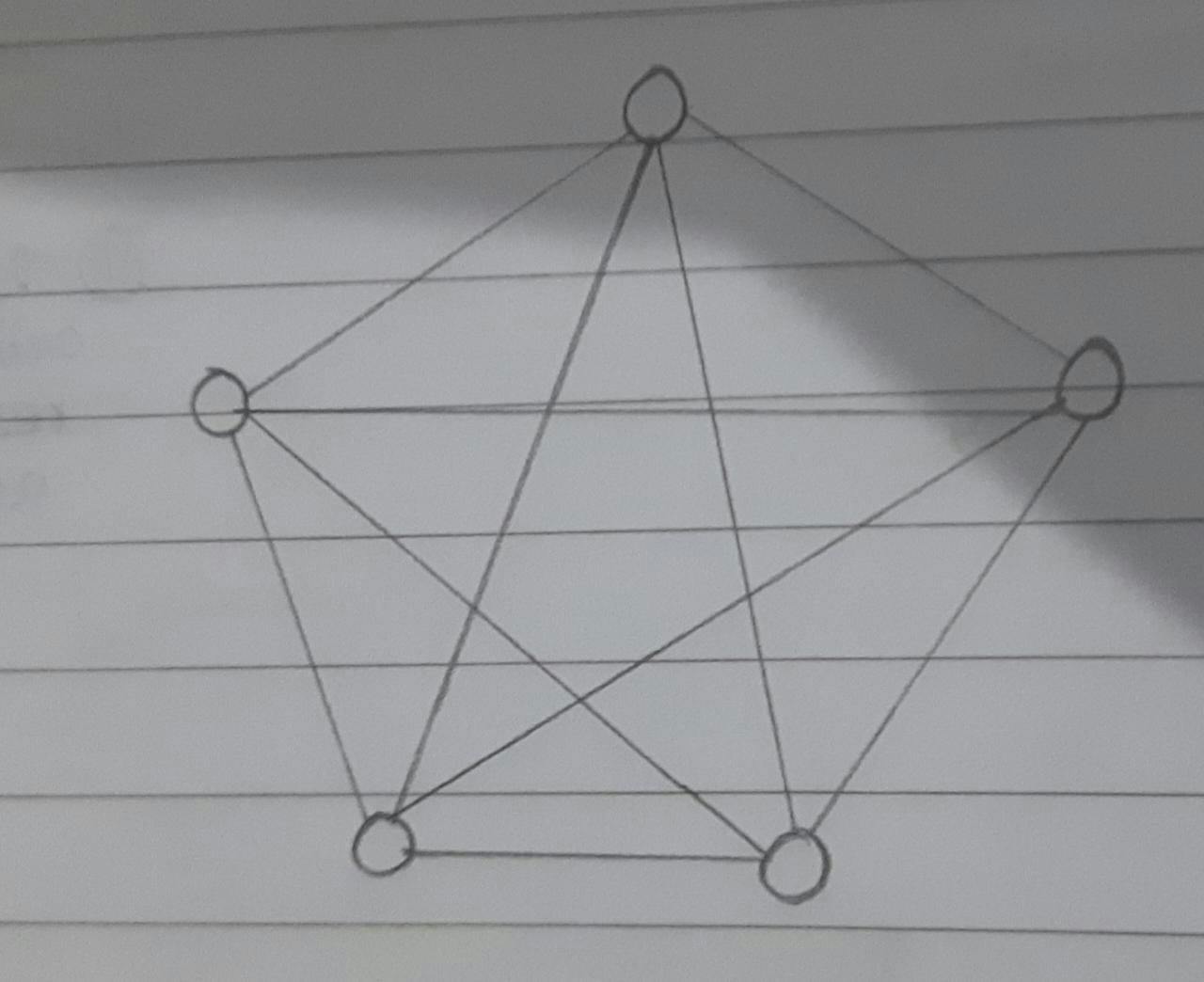
Mesh topology : Every computer will be connected to every single computer.
limitations
-> scalability issues
-> expensive
These were the different kind of topologies
we will learn about OSI model in another blog thank you very much for reading i hope you understood the basic meaning of protocols and networking fundamentals.